Videos
Blogs
Hepatobiliary Cancer Treatment
The hepatobiliary system is comprised of the liver, bile ducts and gallbladder. The hepatobiliary system aids in digestion. The liver is the largest organ in the abdomen and has several essential functions, including detoxification of blood, oxygen storage, metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, etc. The main types of hepatobiliary cancer are hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer), gallbladder cancer, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Factors that increase the risk of hepatobiliary cancer:
As with most cancers, it is hard to pinpoint what causes hepatobiliary cancer. Here are some of the factors that increase the risk of hepatobiliary cancer:
- Liver cirrhosis.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol.
- Chronic viral hepatitis.
- Obesity.
- A history of gallstones or bile duct stones.
- Family history of hepatobiliary cancer.
Types of hepatobiliary cancer:
Browse through for more information on the specific types of hepatobiliary cancers we treat:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer) - The malignant cancer cells form in the liver. The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which affects the primary type of liver cell. The liver purifies and regulates the chemical levels of the body’s bloodstream, maintains blood sugar levels and helps in blood clotting.
- Gallbladder cancer - This is a rare type of cancer where malignant cancer cells form in the gall bladder. The gall bladder and bile duct help break down the fat in the food for digestion in the duodenum.
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma - Bile duct cancer is also referred to as cholangiocarcinoma. This type of cancer occurs in the bile ducts that are seen inside the liver. The bile duct produces a fluid called bile that helps break down food in the small intestine.
- Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma - This is a rare type of cancer that starts in the bile ducts outside the liver. In this, the malignant cancer cells form in the part of the bile ducts outside the liver.
Hepatobiliary cancer is characterised by the following symptoms:
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Gall bladder cancer and Cholangiocarcinoma:
It is important to note that these symptoms do not necessarily point to cancer at all times. Please make an appointment with us if you have any of the above symptoms so we can give you a correct diagnosis.
At Veritas Cancer Care, we employ the latest tests to arrive at a suitable prognosis and formulate a specialised treatment plan based on your needs. We have several methods of diagnosis.
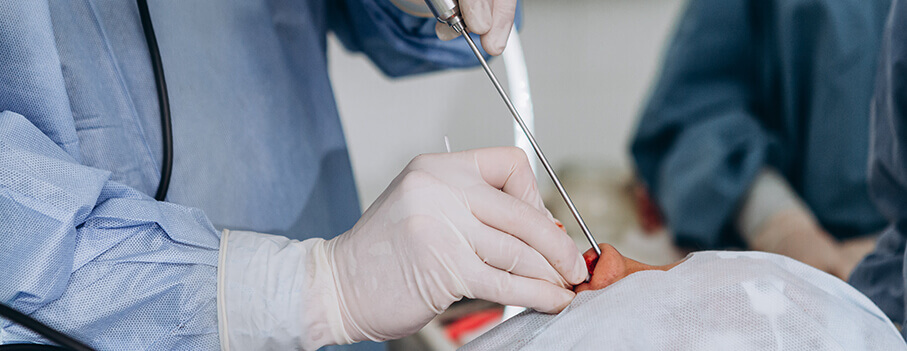
Hepatobiliary cancers can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or immunotherapy. While the primary goal is curing cancer, preserving the surrounding organs and tissues is of utmost importance.
The various treatments options for hepatobiliary cancer include:
Regaining the quality of life of a patient recovering from hepatobiliary cancer can be challenging. At Veritas Cancer Care, we aim to provide our patients with the utmost care and comfort they need during their treatment and remission and improve their quality of life as much as possible. Our team here is dedicated to our patients and, while cancer is a daunting illness, we provide you with all the help and hope you need to recover.
The oncological team at Veritas Cancer Care is headed by Dr Venkat P, a highly-trained surgical oncologist and robotic surgeon, with niche expertise in treating hepatobiliary malignancies. With over 22 years of experience, he has managed around 25,000 oncological cases and performed over 20,000 surgeries. Being one of the very few surgeons in the country highly trained in the latest treatment procedures such as robotic surgery, ERAS and fluorescence-guided surgery, Dr Venkat is a renowned surgical oncologist with various awards to his credit. At Veritas, we guarantee you will receive prompt care and treatment in his safe and experienced hands.